The term “Google algorithm changes” is nothing short of a constant buzz. These changes have a profound impact on the way websites are ranked and how online visibility is established. Here, we will delve into the fascinating world of Google algorithms, exploring their definition, the reasons behind their changes, and an all-encompassing journey through their evolution since their inception.
What is Google Algorithm?
Google Algorithm refers to the complex mathematical formulas and rules employed by the Google search engine to determine the ranking of web pages in search results. These algorithms scrutinize numerous factors, such as relevance, authority, and user experience, to provide users with the most accurate and helpful search results.
Why Does Google Algorithm Change?
Google’s commitment to delivering the best possible search experience motivates constant refinement and updates to its algorithms. The primary objectives behind algorithm changes are as follows:
Enhancing Relevance
Google strives to present users with search results that are highly relevant and aligned with their search intent. Algorithm updates aim to improve the precision and effectiveness of search results by analyzing user behavior and feedback.
Combatting Spam and Manipulation
Over the years, some website owners and SEO practitioners have employed unethical tactics to artificially boost their rankings. Google’s algorithms are continuously refined to counter such spammy techniques and ensure fair play, rewarding high-quality content and genuine user engagement.
Adapting to Technological Advances
The internet landscape is constantly evolving, with new technologies and platforms emerging. Google algorithms must adapt to the changing digital ecosystem, including the rise of mobile usage, voice search, and emerging trends, to provide the best possible search experience.
A Comprehensive History of Google Algorithm Changes
Staying up-to-date with the latest Google algorithm changes is crucial for online success. Google, being the leading search engine, constantly fine-tunes its algorithms to deliver the most relevant and high-quality search results to users worldwide. Understanding the historical changes in Google’s algorithms can shed light on the evolution of SEO practices.
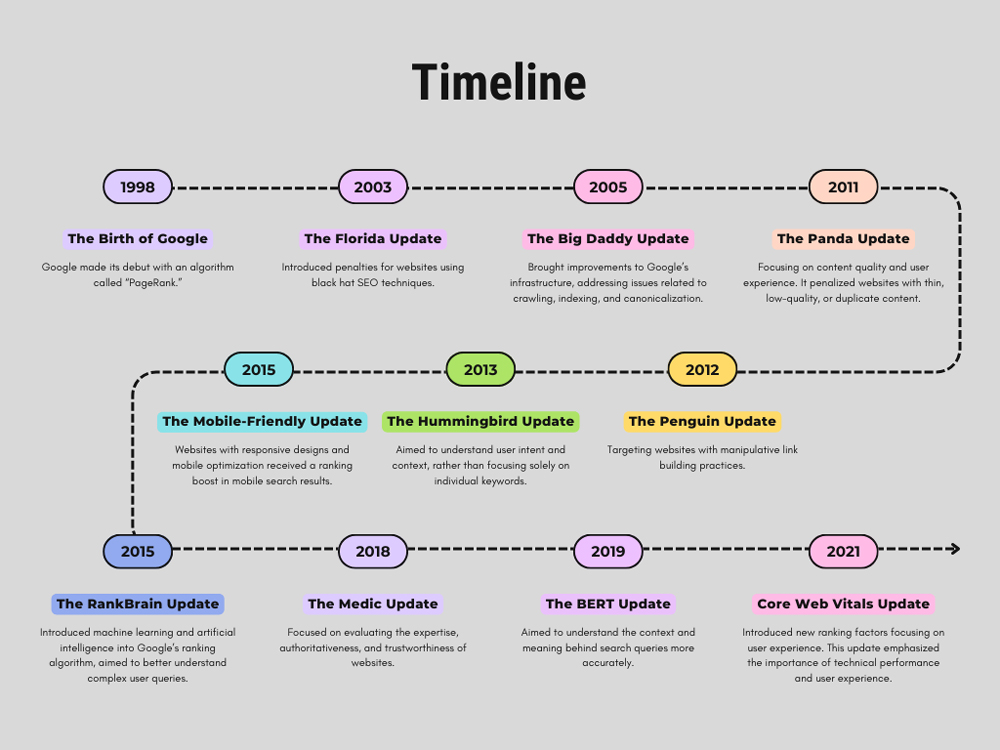
The Birth of Google: PageRank and the Power of Backlinks
In 1998, Google made its debut with an algorithm called “PageRank.” It revolutionized search by evaluating web pages based on the quantity and quality of inbound links they received. PageRank introduced the concept of link authority, prioritizing authoritative websites and shaping the future of SEO.
The Florida Update (November 2003): Quality Content Matters
The Florida update marked a significant shift in Google’s approach. It introduced penalties for websites using black hat SEO techniques, such as keyword stuffing and low-quality content. This update emphasized the importance of quality content and ethical SEO practices.
The Big Daddy Update (December 2005): Crawling, Indexing, and Technical SEO
Big Daddy brought improvements to Google’s infrastructure, addressing issues related to crawling, indexing, and canonicalization. It placed greater emphasis on website architecture, XML sitemaps, and URL canonicalization, laying the foundation for better website optimization and indexation.
The Panda Update (February 2011): Content Quality and User Experience
Panda was a game-changer, focusing on content quality and user experience. It penalized websites with thin, low-quality, or duplicate content while rewarding those with valuable and original content. This update propelled the importance of creating engaging, informative, and user-centric content.
The Penguin Update (April 2012): Link Building and Quality Backlinks
Penguin shook the SEO landscape by targeting websites with manipulative link building practices. It penalized websites engaging in link spamming, link buying, and over-optimization of anchor texts. Penguin emphasized the need for natural and organic link building strategies, promoting the importance of quality backlinks.
The Hummingbird Update (August 2013): Contextual Understanding and Semantic Search
Hummingbird marked a shift toward semantic search and conversational queries. It aimed to understand user intent and context, rather than focusing solely on individual keywords. Hummingbird emphasized the importance of creating content that answers user questions and satisfies their search intent.
The Mobile-Friendly Update (April 2015): Mobile Optimization and User Experience
Recognizing the increasing usage of mobile devices, Google introduced a mobile-friendly update. Websites with responsive designs and mobile optimization received a ranking boost in mobile search results. This update highlighted the significance of mobile optimization for user experience and search rankings.
The RankBrain Update (October 2015): Machine Learning and User Engagement
RankBrain introduced machine learning and artificial intelligence into Google’s ranking algorithm. It aimed to better understand complex user queries and deliver more relevant search results. RankBrain emphasized the importance of user engagement metrics, such as click-through rates and dwell time, in determining rankings.
The Medic Update (August 2018): Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-A-T)
Medic had a significant impact on websites in the health and wellness industry. It focused on evaluating the expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness of websites. Medic highlighted the need for high-quality, authoritative content from trusted sources, especially in sensitive industries.
The BERT Update (October 2019): Contextual Understanding and Natural Language Processing
BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) brought advancements in natural language processing. It aimed to understand the context and meaning behind search queries more accurately. BERT emphasized the importance of creating content that aligns with user intent, rather than solely focusing on keyword optimization.
Core Web Vitals Update (May 2021): User Experience Metrics
In May 2021, Google rolled out the Core Web Vitals update, which introduced new ranking factors focusing on user experience. These include metrics like loading speed (Largest Contentful Paint), interactivity (First Input Delay), and visual stability (Cumulative Layout Shift). This update emphasized the importance of technical performance and user experience in determining search rankings, pushing webmasters to prioritize fast and smooth website functionality.
The Helpful Content Update (August 2022): User-Centric Content
In August 2022, Google launched the Helpful Content Update, which aimed to promote content created for users rather than solely for search engines. It penalized sites that prioritize SEO techniques over providing genuine value to users. This update stressed the need for authentic, useful, and people-first content, reducing the impact of content that seems to exist only to rank.
SpamBrain Integration (December 2022): Enhanced Spam Detection
Google’s ongoing battle against spam continued with the integration of SpamBrain, its AI-powered spam detection system. The December 2022 update focused on reducing the impact of spammy websites and manipulative SEO tactics. Websites that continued to engage in practices like cloaking, sneaky redirects, or keyword stuffing faced stricter penalties, emphasizing the need for ethical SEO practices.
The March 2023 Core Update: Continuous Algorithm Refinement
Google’s March 2023 core update was part of its ongoing efforts to fine-tune search algorithms. While Google didn’t reveal specific details, SEO experts observed changes that affected the ranking of various websites across industries. This update reinforced the importance of maintaining high-quality, authoritative, and relevant content as a key strategy to adapt to core algorithm updates.
The AI-Powered Search Era: SGE (Search Generative Experience)
In 2023, Google introduced its new AI-powered search, known as Search Generative Experience (SGE), aimed at evolving the way search results are presented. This AI-driven feature allows users to receive more context and answers, blending generative AI with traditional search results. This shift has highlighted the increasing importance of intent-driven and user-centered content that aligns with evolving AI functionalities in search.
Conclusion
As we have embarked on this comprehensive exploration of Google algorithm changes, we bear witness to an extraordinary saga of innovation and adaptation. The dynamic nature of Google’s algorithms has played a pivotal role in shaping the SEO landscape. From the inception of PageRank to the emergence of BERT, each algorithmic evolution has propelled the search experience forward, creating a more user-centric and equitable digital realm. As we move forward, it is certain that Google algorithm changes will continue to shape the future of SEO, constantly evolving to meet the ever-changing needs and expectations of users worldwide.





