On-page SEO is the foundation of a successful digital marketing strategy. It involves optimizing every element on your web pages; content, meta tags, headings, and internal links to improve visibility, relevance, and rankings on search engines. By mastering on-page SEO, you can boost organic traffic, enhance user experience (UX), and position your business for long-term success in competitive SERPs.
Ignoring on-page SEO can make even great content invisible to your audience. In this complete guide, you’ll learn what on-page SEO is, why it matters, and the best practices to implement for higher rankings and better user engagement.
What is On-Page SEO?
On-page SEO (or on-site SEO) refers to the process of optimizing individual web pages to improve their visibility and ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs). It focuses on aligning your content and technical elements with user intent and search engine algorithms.
The main goal of on-page SEO is to help search engines understand your page’s context while ensuring users get exactly what they’re looking for. This includes optimizing titles, meta descriptions, keywords, internal links, URLs, and multimedia elements for both readability and relevance.
Why On-Page SEO Matters
Search engines like Google analyze on-page factors to determine the quality, context, and value of a page. Effective on-page SEO ensures your site is easily crawlable, user-friendly, and keyword-relevant; all of which directly impact ranking potential.
Key reasons why on-page SEO matters:
- Improved Rankings: Optimized pages have a higher chance of ranking for targeted keywords.
- Better Click-Through Rates (CTR): Engaging titles and meta descriptions attract more clicks.
- Enhanced Crawlability: Proper structure and linking help search engines index content efficiently.
- Superior User Experience: Well-organized, fast-loading, and mobile-friendly pages retain visitors longer.
- Higher Conversions: Optimized content that matches intent leads to more leads and sales.
Best Practices for On-Page SEO
Implementing best practices for on-page SEO is necessary to achieve higher search engine rankings. By adhering to these practices you can enhance your website’s visibility, improve user experience, and attract targeted organic traffic.
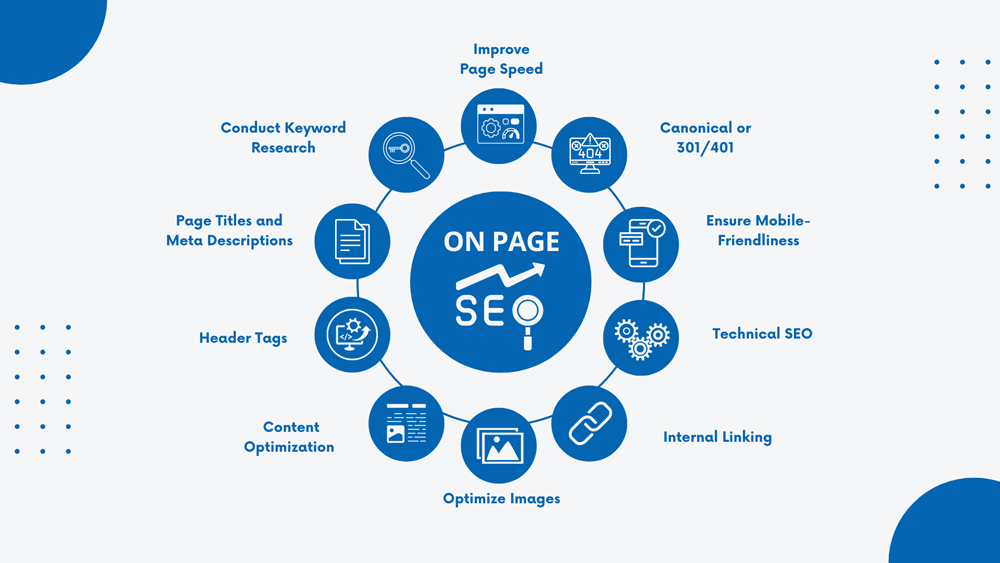
1. Conduct Comprehensive Keyword Research
Start by identifying keywords that align with your audience’s search intent. Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to find high-volume, low-competition terms.
Include a mix of primary, secondary, and LSI (latent semantic indexing) keywords throughout your content naturally.
Pro Tip: Focus on long-tail keywords such as “on-page SEO best practices for small businesses” – they convert better and face less competition.
Learn more about keyword research for SEO.
2. Write Optimized Page Titles and Meta Descriptions
Page titles and meta descriptions are your content’s first impression on Google.
- Keep titles under 60 characters and meta descriptions under 160.
- Include your target keyword near the beginning.
- Use compelling language that encourages clicks.
Example:
Title: On-Page SEO Best Practices: Optimize Your Website Content in 2025
Meta: Discover the latest on-page SEO strategies to boost your rankings, improve UX, and attract organic traffic in 2025.
3. Structure Content with Header Tags (H1, H2, H3)
Header tags help organize your content and make it scannable for both readers and crawlers.
- Incorporate keywords naturally in headers to reinforce relevance.
- Use H1 for the main topic (only once).
- Use H2 for subtopics and H3 for supporting details.
4. Create High-Quality, Keyword-Rich Content
Your content should deliver value, address search intent, and engage the reader.
- Aim for at least 1,000–1,500 words per core topic.
- Use keywords naturally, avoid stuffing.
- Include internal and external links for credibility and context.
- Update older posts regularly to stay relevant.
Google’s Helpful Content Update emphasizes that content must be written for people, not algorithms. Always prioritize user value.
Learn more about content writing strategy.
5. Optimize Images for SEO
Images enhance engagement but can also slow down your site if not optimized.
- Use WebP format for lighter, high-quality visuals.
- Use descriptive filenames and alt text with relevant keywords.
- Compress files using TinyPNG or ShortPixel to improve page speed.
Learn more about image optimization for SEO.
6. Use Internal Linking Strategically
Internal links distribute link equity, help crawlers find content, and guide users through your site.
- Link to cornerstone or high-converting pages.
- Use descriptive anchor text (avoid “click here”).
- Audit and fix broken internal links regularly.
Example:
Instead of “Read more,” use: Learn how to build a strong website structure for better SEO.
Learn more about internal linking for SEO.
7. Improve Page Speed and Core Web Vitals
Fast-loading pages lead to higher engagement and better rankings.
- Use Google PageSpeed Insights to monitor Core Web Vitals (LCP, FID, CLS).
- Compress media, leverage caching, and use a CDN (Content Delivery Network).
- Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML.
Learn more about Google Core Web Vitals.
8. Ensure Mobile Optimization and Responsiveness
With mobile-first indexing, Google primarily ranks your mobile version.
- Test your site using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test Tool.
- Use responsive design that adapts to any device.
- Keep navigation simple and touch-friendly.
9. Include Schema Markup for Rich Results
Schema markup helps Google understand your content and display rich snippets (e.g., FAQs, reviews, events).
- Implement FAQ, Article, Product, or BreadcrumbList schema.
- Validate markup using Google’s Rich Results Test.
Learn more about Google schema markup.
Pro Insight
Use content optimization tools like Surfer SEO, Clearscope, or Frase to analyze top-ranking pages. These tools provide real-time recommendations for keyword density, structure, and related terms; helping you outrank competitors strategically.
Conclusion
On-page SEO is not just about inserting keywords; it’s about creating a seamless experience for users and search engines alike. By following these best practices, you’ll strengthen your website’s structure, increase organic visibility, and stay ahead of competitors in 2025.
Remember: consistency, quality, and technical precision are key to long-term SEO success.
Frequently Asked Questions
On-page SEO focuses on optimizing elements within your website (content, structure, meta tags), while off-page SEO deals with external factors like backlinks and domain authority.
You should perform an SEO audit every 3–6 months. Refresh your keywords, update meta tags, and fix any broken links or outdated content.
Recommended tools: Yoast SEO, Rank Math, Google Search Console, Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Screaming Frog.
Track your performance using Google Search Console, analytics tools, and keyword ranking reports. Look for improvements in CTR, dwell time, and organic traffic.